
Machine learning has become an integral part of our daily lives, revolutionizing various industries and shaping the future of technology. From personal assistants to self-driving cars, machine learning algorithms are powering countless applications that make our lives easier and more efficient. (Let’s explore this topic in more detail with 2048 Game below)
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating algorithms and models that can learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. Unlike traditional programming, where rules are explicitly defined, machine learning systems can improve their performance over time through experience and exposure to new information.
At its core, machine learning relies on three main components: data, algorithms, and computational power. The data serves as the foundation for learning, providing the necessary information for the system to identify patterns and make predictions. Algorithms are the mathematical models that process this data and generate insights. Computational power enables these algorithms to process vast amounts of information quickly and efficiently.
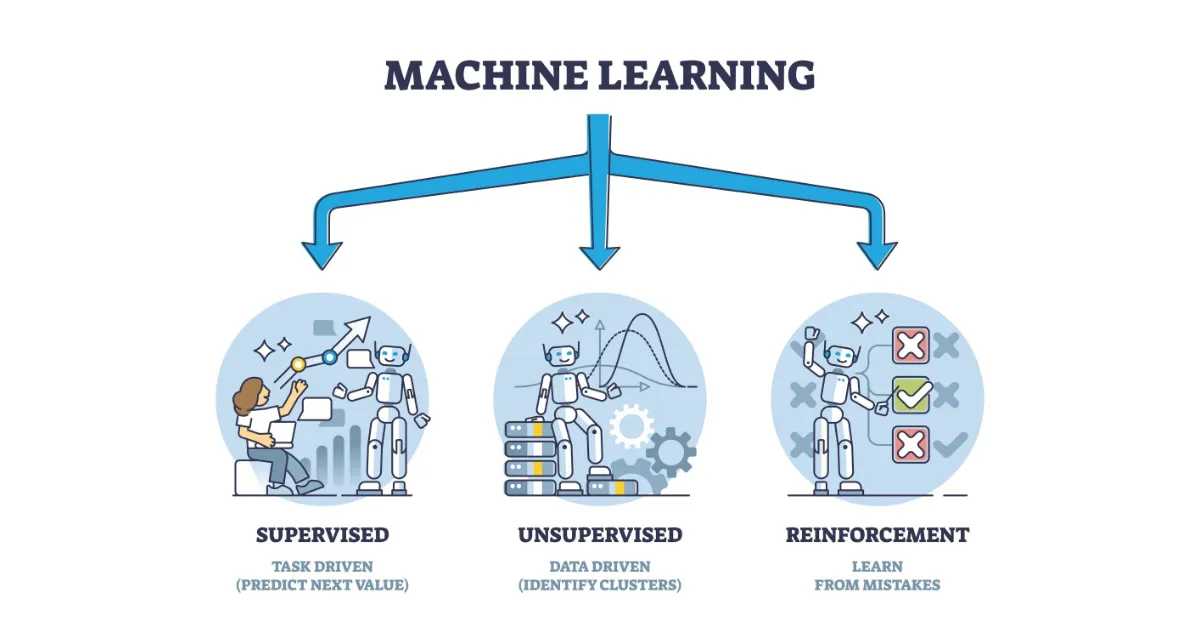
There are several types of machine learning, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data, where the correct outputs are known in advance. Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, deals with unlabeled data and aims to discover hidden patterns or structures within the information. Reinforcement learning focuses on training models to make decisions in dynamic environments through trial and error.
Read more: Can AI Replace Software Developers in the Future
Machine learning has found its way into numerous aspects of our daily routines, often without us even realizing it. One of the most common applications is in recommendation systems, such as those used by streaming platforms like Netflix or e-commerce giants like Amazon. These systems analyze our viewing or shopping habits to suggest content or products tailored to our preferences.
In the realm of personal assistants, machine learning powers voice recognition and natural language processing capabilities. Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use these technologies to understand and respond to our voice commands, making tasks like setting reminders or searching for information more convenient.
The healthcare industry has also benefited greatly from machine learning. Algorithms can analyze medical images to detect diseases, predict patient outcomes, and even assist in drug discovery. In finance, machine learning models are used for fraud detection, credit scoring, and algorithmic trading.
As machine learning continues to advance, we can expect to see even more transformative applications in the coming years. One area of significant interest is the development of more sophisticated natural language processing models, such as GPT-3, which can generate human-like text and have the potential to revolutionize content creation and language translation.
Another exciting frontier is the field of computer vision, where machine learning algorithms are becoming increasingly adept at understanding and interpreting visual information. This technology is crucial for the development of autonomous vehicles, facial recognition systems, and augmented reality applications.
The convergence of machine learning with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing, is also opening up new possibilities. By processing data closer to its source, these systems can make real-time decisions and adapt to changing environments more efficiently.
As machine learning becomes more prevalent in our lives, it’s essential to address the ethical considerations and challenges that come with this technology. One major concern is the potential for bias in machine learning models, which can perpetuate or exacerbate existing societal inequalities. Ensuring fairness and transparency in these systems is crucial for their responsible development and deployment.
Data privacy is another significant issue, as machine learning algorithms often require large amounts of personal information to function effectively. Striking a balance between data collection for improved performance and protecting individual privacy rights is an ongoing challenge for researchers and policymakers.
While machine learning has made remarkable progress in recent years, it’s important to recognize that human expertise still plays a crucial role in its development and application. Data scientists and machine learning engineers are responsible for designing algorithms, selecting appropriate models, and interpreting results.
Moreover, the human touch is often necessary to provide context and nuance in decision-making processes that rely on machine learning outputs. As we continue to integrate these technologies into various aspects of our lives, fostering a symbiotic relationship between human intelligence and artificial intelligence will be key to maximizing their potential benefits.
The convergence of machine learning with smart home technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT) has ushered in a new era of intelligent living spaces. These advanced systems are capable of learning from user behavior, adapting to preferences, and optimizing various aspects of home management.
One of the primary applications of machine learning in smart homes is energy management. By analyzing patterns of energy consumption and factoring in variables such as weather conditions and occupancy, these systems can automatically adjust heating, cooling, and lighting to maximize efficiency and reduce costs. Some smart thermostats, for example, use machine learning algorithms to create personalized schedules based on users’ habits and preferences.
Security is another area where machine learning is making significant strides in smart home technology. Advanced surveillance systems can use computer vision algorithms to distinguish between normal activity and potential threats, alerting homeowners or authorities when suspicious behavior is detected. These systems can also learn to recognize familiar faces and vehicles, reducing false alarms and enhancing overall security.
Voice-controlled smart home assistants, such as Amazon’s Alexa or Google Home, rely heavily on machine learning for natural language processing and voice recognition. These devices continually improve their understanding of user commands and preferences, offering increasingly personalized and accurate responses over time.
In the realm of home automation, machine learning algorithms can create sophisticated routines that anticipate users’ needs. For instance, a smart home system might learn that you typically arrive home from work at 6 PM and automatically adjust the temperature, turn on lights, and start brewing coffee a few minutes before your arrival.
The proliferation of IoT devices in smart homes has led to an explosion of data, creating both opportunities and challenges for machine learning applications. Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to its source rather than sending it to centralized cloud servers, is becoming increasingly important in this context.
By leveraging edge computing, smart home devices can make real-time decisions and respond to changes in the environment more quickly. This is particularly crucial for applications that require low latency, such as security systems or emergency response features. Additionally, processing data locally can help address privacy concerns by reducing the amount of sensitive information transmitted over networks.
Machine learning models deployed on edge devices can also adapt to specific household environments more effectively. For example, a smart air purifier might use local sensors and machine learning algorithms to optimize its performance based on the unique air quality conditions of a particular home.
As IoT devices become more sophisticated and interconnected, machine learning will play a vital role in managing and orchestrating these complex ecosystems. Smart home hubs and central control systems will increasingly rely on AI to coordinate various devices, resolve conflicts, and create seamless user experiences.
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning are at the forefront of technological innovation, driving advancements across various industries and shaping the future of how we live and work. As these technologies continue to evolve, their impact on future tech is becoming increasingly profound and far-reaching.
One of the most significant areas of development is in the field of autonomous systems. Self-driving cars, drones, and robots are becoming more sophisticated thanks to advances in machine learning algorithms. These systems can process vast amounts of sensor data in real-time, make complex decisions, and adapt to changing environments. As they become more reliable and widespread, we can expect to see major transformations in transportation, logistics, and manufacturing.
In healthcare, AI and machine learning are revolutionizing diagnosis, treatment, and drug discovery. Machine learning models can analyze medical images with incredible accuracy, often outperforming human experts in detecting certain conditions. AI-powered systems are also being used to predict patient outcomes, optimize treatment plans, and accelerate the development of new medicines. As these technologies advance, we may see more personalized and effective healthcare solutions.
The financial sector is another area where AI and machine learning are making significant inroads. Algorithmic trading systems powered by machine learning can analyze market trends and execute trades at speeds impossible for human traders. AI is also being used to detect fraud, assess credit risk, and provide personalized financial advice. In the future, we may see AI playing an even larger role in financial decision-making and risk management.
Read more: The Role of AI in Healthcare Breakthroughs
One of the most exciting developments in AI is the field of generative AI, which includes technologies like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) models. These systems can generate human-like text, create realistic images, and even compose music. As generative AI continues to improve, we can expect to see its application in various creative fields, potentially transforming content creation, design, and entertainment industries.